Navisys Technology Corp. 2020/03 GPSサポート

マルチ受信GNSS GPS/QZSS/Galileo/GLONASS or GPS/QZSS/Galileo/BEIDOU
QZSS L1S SLAS (サブメータ級測位補強サービス) サポート
IMES (屋内測位システム) サポート
補強システム QZSS & SBAS (WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS, GAGAN)
自律航法(ケーブルレス)IMU(慣性計測ユニット)内蔵
入力 RTCM 10402.3 Message 1,2,3,9
防水 IPX7
QZSS SLAS(Sub meter Level Augmentation Service)は、GPSとQZSS衛星の疑似距離の補正データを提供する拡張技術です。 SLASを有効にすると、GR 8017はユーザーの要求に基づいて、最適な地上監視局(GMS)を自律的に選択します。 そして、このGMSの補正ストリームを測定値に適用し、位置を改善します。 生の測定データは受信機がデータビットの同期と週の時間を確立すると利用可能になります。 メッセージ・データは、データ・ビットとフレームの同期をとるのに十分なレベルで追跡されたすべての信号について利用可能です。 フレーム同期を実現するのに十分なレベルで追跡されたすべての信号について、メッセージデータが利用できます。
NEO-M8UをベースとしたGR-8017のUntethered Dead Reckoning(UDR)ソリューションは、GNSSが使えない場所や短時間のGNSS停止時にも優れたナビゲーション性能を発揮します。UDRは、慣性航法装置(INS)とGNSS計測を統合したSFDR(Sensor Fusion Dead Reckoning)技術をベースにしています。INSは、慣性計測ユニット(IMU)によって感知された角速度と特定の力を統合します。INSは、位置、速度、姿勢の変化を計算し、初期化されれば正確なナビゲーション情報を提供することができる。しかし、慣性のみのナビゲーションソリューションでは、IMUの観測値に誤差が生じるため、時間の経過とともに劣化してしまいます。INSとGNSS測定を統合することで、INSを較正することにより、時間とともに増大する誤差を抑えることができます。このようにして得られたINS/GNSS統合フィルター(以下、フュージョン・フィルターと呼ぶ)は、スタンドアローンのGNSS測位と比較して、以下のような利点がある。 GNSSが使えない状況でのナビゲーション性能の向上:マルチパスによる誤差 NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017 5 マルチパスや信号が弱い状態でも、IMUの補助により誤差が軽減されます。 短時間のGNSS停止時のナビゲーションソリューション:トンネルや駐車場などで発生する短時間のGNSSギャップをINSが埋めます。 NEO-M8Uを搭載した「GR-8017」は、GNSSとIMUの測定値を組み合わせ、最大2Hzのレートでポーションソリューションを算出します。これらのソリューションは、標準的なNMEA、UBX-NAV-PVT!および関連メッセージで報告されます。新しいHigh Navigation Rate出力メッセージ(UBX-HNR-PVT)は、これらの結果をIMUのみのデータで拡張し、最大30Hzのレートで正確かつ低レイテンシーの位置ソリューションを提供します。 推測航法では、モジュールに電源を投入すると同時に(つまり、GNSSの固定が確立する前に)、以下のすべての条件を満たす場合にナビゲーションを開始することができます。 モジュールに電源が供給されていない状態で車両が移動していないこと 車両が最後に使用されたときに、少なくともデッドレコニング固定が可能であった。 車両が最後に使用されたときからモジュールにバックアップ電源が供給されている。 後処理用のセンサデータは,ESF(External Sensor Fusion)クラスのメッセージ UBX-ESF-MEAS および UBX-ESF-RAW(high rate)から取得できます。各メッセージには、測定時刻が含まれています。 ! このドキュメントの uu--blox のバイナリ・メッセージは、「uu--blox M8 Receiver Description blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specificationプロトコル仕様を含む」で説明されていますが、「4.74.7」を参照してください。 www.DeepL.com/Translator(無料版)で翻訳しました。
原子時計と地球の自転が同期しているため、数年ごとにうるう秒の調整が行われます。
通常このような調整は、チップ発売前に校正されます。
チップ発売後も複数回のうるう秒調整が行われる可能性があります。チップは
このようなうるう秒の調整は、チップが正確な時計とうるう秒の情報を取得した後、自動的に行われます。
閏秒が調整されたかどうかを知るには以下のバイナリコマンドを問い合わせ (UBX NAV TIMEGP S)
B5 62 01 20 00 00 21 64
チップは次の2つのようなバイナリメッセージを返します。
チップは次の2つのようなメッセージを返します。
B5 62 01 20 10 00 80 09 47 07 87 6a 06 00 22 07 0f 03 0c 00 00 46 500c 00 00 46 50
B5 62 01 20 10 00 60 db 56 07 ac 5f ff f 22 07 10 07 09 00 00 18 4509 00 00 18 45
bytの値を確認します。
赤色で表示されている18バイトの値を確認し、その値が07であれば、GPS時刻調整済み
それ以外の場合(例:3, 1, 0)(例:3, 1, 0)では、未調整です。
| GPS |
u-blox GNSS ultra performance Module M8U
|
| 受信方式 |
72チャンネル
|
| 加速度 |
<4g
|
| 高度 |
50,000m limit
|
| 速度 |
500m/秒 1,852Km/hr limit
|
| 正確度 |
速度0.05m/秒 進行方位1度
|
| 受信周波数 |
GPS L1 C/A, SBAS L1 C/A, QZSS L1 C/A, QZSS L1-SAIF
|
| 受信感度 |
-160dBm(GPS GLONASS tracking) -148dBm(GPS GLONASS測位時)
|
| 水平位置 |
2.5m (単独) 1.5m(SBAS)
|
| 更新レート |
2Hz(GNSS&IMU 初期1Hz)) 30Hz(UBX UBX-HNR-PVT初期無し)
|
| TTFF |
25秒 Cold 1秒 Hot
|
| 出力メッセージ |
NMEA 0183(2.3/4.x), UBX ,Input-RTCM2.3 1,2,3,9
|
| Raw Data |
RXM-RAWX 搬送波位相 RXM-SFRBX 各衛星航法データ
|
| ボーレート |
9600bps default N-8-1
|
| 電源電圧 |
DC5V (33mA 標準)USB2.0
|
| 本体サイズ |
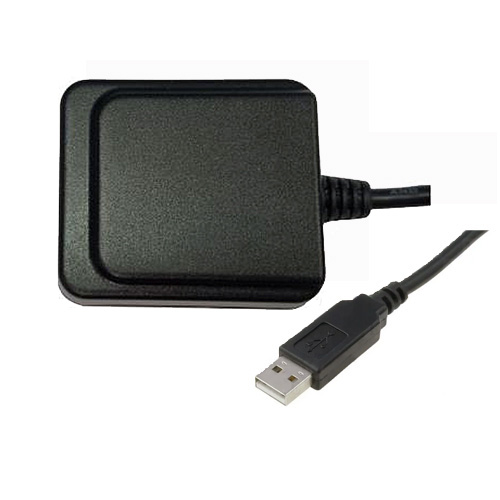
40mm x 45㎜ x18mm
|
| ケーブル |
USB Type A 1.5m
|
| インターフェイス |
USB(Windows USB serial Driver)/Sensor(u-blox GNSS Sensor Device Driver for Windows)
|
| ストレージ温度 |
-40℃~85℃
|
| バッテリ温度 |
-20℃~60℃
|
| 湿度 |
95%(結露しない)
|
| 防水 |
IPX7
|
| 振動 |
5Hz-500Hz 5g
|
| 振動正弦半波衝撃パルス |
30g 11ms
|
| Certification |
RoHS
|
| USB A Type |
Pin 1 Vin Pin2,3 USB IF Pin4 GND
|
| LED Color |
LED(赤) ON 探索中 LED(赤)点滅 捕捉完了
|

u-center 21.0.5
├── File
├── Edit
├── View
├── Packet Console
├── Binary Console
├── Text Console
├── Message View
├── Configuration View
├── (Generation 9 Configuration View)
├── Statics View
├── Table View
├── Recent Table View
├── Chart View
├── Recent Chart View
├── Histgram View
├── Recent Histgram View
├── (GNSS Driver View)
├── Map View
├── Recent Static Map View
├── Camera View
├── Daviation Map
├── Sky View
├── Docking Windows
└── Toolbars
├── Player
├── Reciver
├── Connection
├── Baudrate
├── Tools
├── Windows
└── Help
GR8017 supports both NMEA text messages and UBX binary messages. In this section, the
NMEA output messages are discussed. For UBX binary messages , please refer to u blox Re-
ceiver Description Protocol Spec.
3.1 NMEA Output Messages
Multi
t alker IDs ar e used in GNSS multi satellite positioning systems
Talker ID is ‘GP’ for GPS specific sentences
Talker ID is ‘GL’ for GLONASS specific sentences
Talker ID is ‘GB’ for BEIDOU specific sentences
Talker ID is ‘GN’ is used for generic GNSS sentences
System\Sentence
GPGGA
GPGLL
GPGSA
GPGSV
GPRMC
GPVTG
GLGGA
GLGLL
GLGSA
GLGSV
GLRMC
GLVTG
GBGGA
GBGLL
GBGSA
GBGSV
GBRMC
GBVTG
GNGGA
GNGLL
GNGSA
GPGSV GLGSV
GNRMC
GNVTG
GNGGA
GNGLL
GNGSA
GPGSV GBGSV
GNRMC
GNVTG
The NMEA0183 Output Messages are shown as below:
NMEA Record
Descriptions
GxGGA:Global positioning system fixed data: time, position, fixed type
GxGLL:Geographic position: latitude, longitude, UTC time of position fix and status
GxGSA:GPS receiver operating mode, active satellites, and DOP values
GxGSV:GNSS satellites in view: ID number, elevation, azimuth, and SNR values
GxRMC:Recommended minimum specific GNSS data: time, date, position, course, speed
GxVTG:Course over ground and ground speed
GxGNS:GNSS fix data
GxGRS:GNSS range residuals
GxGST:GNSS pseudo range error statistics
GxTXT:u-blox message
The GR-8017 adopts interface protocol of National Marine Electronics Association's NMEA-0183 Version 2.3 & 4.x interface specification.
GR-8017 supports multiple types of NMEA sentences (GxGGA, GxGLL, GxGSA, GxGSV, GxRMC, GxVTG, GxGNS, GxGRS, GxGST, GxZDA, and GxTXT).
The default output sentences are RMC, VTG, GNS, GGA, GSA, GSV, GLL, GST, and ZDA
GPS message examples:
$GPRMC,065500.00,A,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,15.869,189.32,051109,,,D*57
$GPVTG,189.32,T,,M,15.869,N,29.405,K,D*30
$GPGGA,065500.00,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,2,12,0.91,69.8,M,16.3,M,,*65
$GPGSA,A,3,20,02,23,13,50,42,04,11,17,28,32,08,1.53,0.91,1.22*0D
$GPGSV,4,1,13,02,10,252,26,04,39,268,40,08,09,197,41,11,17,058,32*7B
$GPGSV,4,2,13,13,06,144,23,17,50,345,43,20,45,056,44,23,11,109,37*72
$GPGSV,4,3,13,27,02,301,,28,73,194,39,32,20,043,38,42,54,140,34*7B
$GPGSV,4,4,13,50,51,133,33*4B $GPGLL,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,065500.00,A,D*6E
$GPTXT,01,01,02,u-blox ag - www.u-blox.com*50
GLONASS message examples:
$GLRMC,031809.00,V,,,,,,,050913,,,N*6C
$GLVTG,,,,,,,,,N*2C
$GLGGA,031809.00,,,,,0,04,1.76,,,,,,*4D
$GLGSA,A,1,81,79,77,82,,,,,,,,,4.23,1.76,3.84*1B
$GLGSV,2,1,06,77,26,149,33,78,79,127,,79,39,336,32,81,59,299,35*6F
$GLGSV,2,2,06,82,23,242,33,88,33,020,*6E
$GLGLL,,,,,031809.00,V,N*55
$GLRMC,031810.00,A,2446.42259,N,12100.44836,E,0.265,,050913,,,A*6B
$GLVTG,,T,,M,0.265,N,0.491,K,A*32
$GLGGA,031810.00,2446.42259,N,12100.44836,E,1,05,1.29,133.2,M,16.3,M,,*40
$GLGSA,A,3,81,79,88,77,82,,,,,,,,3.50,1.29,3.26*18
$GLGSV,2,1,06,77,26,149,34,78,79,127,26,79,39,336,33,81,59,299,35*6D
$GLGSV,2,2,06,82,23,242,33,88,33,020,28*64
$GLGLL,2446.42259,N,12100.44836,E,031810.00,A,A*7D
GPS+GLONASS message examples:
$GNRMC,052449.00,V,,,,,,,211114,,,N*6B
$GNVTG,,,,,,,,,N*2E
$GNGGA,052449.00,,,,,0,00,99.99,,,,,,*76
$GNGSA,A,1,,,,,,,,,,,,,99.99,99.99,99.99*2E
$GNGSA,A,1,,,,,,,,,,,,,99.99,99.99,99.99*2E
$GPGSV,4,1,13,02,,,44,05,,,46,06,,,44,07,,,37*7E
$GPGSV,4,2,13,10,,,43,12,,,34,13,,,44,15,,,33*79
$GPGSV,4,3,13,26,,,44,29,,,37,30,,,41,42,,,40*73
$GPGSV,4,4,13,50,,,38*75
$GLGSV,1,1,02,86,,,39,,,,35*65
$GNGLL,,,,,052449.00,V,N*5A
$GNRMC,052449.97,A,2446.42460,N,12100.44230,E,0.036,,211114,,,A*6E
$GNVTG,,T,,M,0.036,N,0.066,K,A*38
$GNGGA,052449.97,2446.42460,N,12100.44230,E,1,08,1.51,113.9,M,16.3,M,,*42
$GNGSA,A,3,02,05,06,10,13,26,30,,,,,,2.78,1.51,2.33*13
$GNGSA,A,3,86,,,,,,,,,,,,2.78,1.51,2.33*18
$GPGSV,4,1,13,02,64,033,44,05,57,324,46,06,37,094,44,07,,,37*42
$GPGSV,4,2,13,10,31,042,43,12,,,35,13,60,070,44,15,,,33*7D
$GPGSV,4,3,13,26,48,188,44,29,,,37,30,13,099,40,42,54,141,40*48
$GPGSV,4,4,13,50,51,133,38*40
$GLGSV,1,1,02,86,19,151,39,,,,34*59
$GNGLL,2446.42460,N,12100.44230,E,052449.97,A,A*74
BEIDOU message examples:
$GBRMC,085705.00,V,,,,,,,021214,,,N*64
$GBVTG,,,,,,,,,N*22
$GBGGA,085705.00,,,,,0,00,2.36,,,,,,*4C
$GBGSA,A,1,,,,,,,,,,,,,11.48,2.36,11.24*1F
$GBGSV,1,1,00*6B
$GBGLL,,,,,085705.00,V,N*57
$GBRMC,085706.00,A,2446.41030,N,12100.43907,E,0.031,,021214,,,A*61
$GBVTG,,T,,M,0.031,N,0.058,K,A*3E
$GBGGA,085706.00,2446.41030,N,12100.43907,E,1,00,2.36,118.7,M,16.3,M,,*47
$GBGSA,A,3,,,,,,,,,,,,,11.48,2.36,11.24*1D
$GBGSV,1,1,00*6B
$GBGLL,2446.41030,N,12100.43907,E,085706.00,A,A*7E
GPS+BEIDOU message examples:
$GNRMC,062331.00,V,,,,,,,041214,,,N*64
$GNVTG,,,,,,,,,N*2E
$GNGGA,062331.00,,,,,0,00,99.99,,,,,,*7D
$GNGSA,A,1,,,,,,,,,,,,,99.99,99.99,99.99*2E
$GNGSA,A,1,,,,,,,,,,,,,99.99,99.99,99.99*2E
$GPGSV,3,1,09,02,,,45,05,,,46,10,,,38,13,,,42*78
$GPGSV,3,2,09,15,,,47,24,,,39,26,,,48,29,,,42*7F
$GPGSV,3,3,09,30,,,41*76
$GBGSV,2,1,06,401,,,40,402,,,35,403,,,39,404,,,37*66
$GBGSV,2,2,06,406,,,39,409,,,39*62
$GNGLL,,,,,062331.00,V,N*51
$GNRMC,062332.00,A,2446.42524,N,12100.43953,E,0.040,,041214,,,A*65
$GNVTG,,T,,M,0.040,N,0.075,K,A*3B
$GNGGA,062332.00,2446.42524,N,12100.43953,E,1,08,1.11,117.9,M,16.3,M,,*4C
$GNGSA,A,3,02,05,13,15,24,26,30,29,,,,,1.94,1.11,1.59*17
$GNGSA,A,3,,,,,,,,,,,,,1.94,1.11,1.59*1C
$GPGSV,3,1,09,02,43,131,45,05,44,042,46,10,03,082,37,13,31,036,42*7B
$GPGSV,3,2,09,15,58,250,47,24,14,185,39,26,72,017,48,29,39,270,42*70
$GPGSV,3,3,09,30,12,050,41*40
$GBGSV,2,1,06,401,,,40,402,,,35,403,,,39,404,,,37*66
$GBGSV,2,2,06,406,,,39,409,,,39*62
$GNGLL,2446.42524,N,12100.43953,E,062332.00,A,A*7A
3.2 GxGGA - Global Positioning System Fix Data
Example $GPGGA,065500.00,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,2,12,0.91,69.8,M,16.3,M,,*65
Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPGGA
GGA protocol header
UTC Time
065500.00
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Latitude
2447.65027
ddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
North/South
N
N: North Latitude, S: South Latitude
Longitude
12100.78318
dddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
East/West
E
E: East Longitude, W: West Longitude
Position Fix Indicator
2
0: Fix not available or invalid,
1: GPS SPS Mode, fix valid,
2: Differential GPS, SPS Mode, fix valid,
3: Not supported,
4: RTK fixed
5: RTK float
6: Estimated/Dead Reckoning fix
Satellites Used
12
Number of satellites used in positioning calculation (0 to 12)
HDOP
0.91
Horizontal Dilution of Precision
MSL Altitude
69.8
meters
Unit
M
Meters
Geoidal separation
16.3
meters
Geoid separation: difference between ellipsoid and mean sea level
Units
M
Meters
Age of Diff. Corr.
second
Age of differential corrections. Null when DGPS is not used
Diff. Ref. Station ID
ID of station providing differential corrections (null when DGPS is not used)
checksum
*65
End of sentence
3.3 GxGLL - Geographic Position - Latitude / Longitude
Example
$GPGLL,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,065500.00,A,D*6E
Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPGLL
GLL protocol header
Latitude
2447.65027
ddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
North/South
N
N: North Latitude, S: South Latitude
Longitude
12100.78318
dddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
East/West
E
E: East Longitude, W: West Longitude
UTC Time
065500.00
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Status
A
A: Data valid, V: Data invalid
Mode Indicator
D
A: Autonomous GNSS fix
N: No position fix
D: Differential GNSS fix
E: Estimated/Dead reckoning fix
F: RTK float
R: RTK fixed
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
14
checksum
*6E
End of sentence
3.4 GxGSA - GNSS DOP and Active Satellites
Example
$GPGSA,A,3,20,02,23,13,50,42,04,11,17,28,32,08,1.53,0.91,1.22*0D
Explanation
Contents
Example
Explanation
Message ID
$GPGSA
GSA protocol header
Mode 1
A
M: Manual—forced to operate in 2D or 3D mode
A: 2D Automatic—allowed to automatically switch 2D/3D
Mode 2
3
1: Fix not available
2: 2D (<= 4 Satellites used)
3: 3D (>= 4 Satellites used)
Satellite used in solution
20
Satellite on Channel 1
Satellite used in solution
02
Satellite on Channel 2
…
Display of quantity used (12 max)
If less than 12 SVs are used for navigation, the remaining fields are left empty. If more than 12 SVs are used for navigation, only the IDs of the first 12 are output.
PDOP
1.53
Position Dilution of Precision
HDOP
0.91
Horizontal Dilution of Precision
VDOP
1.22
Vertical Dilution of Precision
checksum
*0D
End of sentence
3.5 GxGSV - GNSS Satellites in View
Example
$GPGSV,4,1,13,02,10,252,26,04,39,268,40,08,09,197,41,11,17,058,32*7B $GPGSV,4,2,13,13,06,144,23,17,50,345,43,20,45,056,44,23,11,109,37*72 $GPGSV,4,3,13,27,02,301,,28,73,194,39,32,20,043,38,42,54,140,34*7B $GPGSV,4,4,13,50,51,133,33*4B
Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPGSV
GSV protocol header
Number of messages
4
Range 1 to 4
Message number
1
Range 1 to 4
Satellites in view
13
Number of satellites visible from receiver
Satellite ID number
02
Channel 2 (Range 1 to 64)
The satellite ID numbers are in the range of 1 to 32 for GPS satellites, and 33 to 64 for SBAS satellites (ID=120-PRN; e.g. SV ID 33 is SBAS PRN 120, 34 is SBAS PRN 121, and so on). ID numbers 65~96 for GLONASS. ID numbers 193~197 for QZSS.
ID numbers 401~437 for BEIDOU.
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
15
Elevation
10
degrees
Elevation angle of satellite as seen from receiver channel 1 (00 to 90)
Azimuth
252
degrees
Satellite azimuth as seen from receiver channel 1 (000 to 359)
SNR (C/No)
26
dBHz
Received signal level C/No from receiver channel 1 (00 to 99, null when not tracking)
…
Satellite ID number
11
Channel 4 (Range 1 to 32)
The satellite ID numbers are in the range of 1 to 32 for GPS satellites, and 33 to 64 for SBAS satellites (ID=120-PRN; e.g. SV ID 33 is SBAS PRN 120, 34 is SBAS PRN 121, and so on). ID numbers 65~96 for GLONASS. ID numbers 193~197 for QZSS.
ID numbers 401~437 for BEIDOU.
Elevation
17
degrees
Elevation angle of satellite as seen from receiver channel 4 (00 to 90)
Azimuth
058
degrees
Satellite azimuth as seen from receiver channel 4 (000 to 359)
SNR (C/No)
32
dBHz
Received signal level C/No from receiver channel 4 (00 to 99, null when not tracking)
checksum
*71
End of sentence
3.6 GxRMC - Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data
Example
$GPRMC,065500.00,A,2447.65027,N,12100.78318,E,15.869,189.32,051019,,,D*57
Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPRMC
RMC protocol header
UTC Time
065500.00
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Status
A
A: Data valid, V: Data invalid
Latitude
2447.65027
ddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
North/South
N
N: North Latitude, S: South Latitude
Longitude
12100.78318
dddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
East/West
E
E: East Longitude, W: West Longitude
Speed over ground
15.869
knots
Receiver’s speed
Course over ground
189.32
degrees
Receiver’s direction of travel
Moving clockwise starting at due north
Date
051019
ddmmyy
dd: Day, mm: Month, yy: Year
Magnetic variation
degrees
This receiver does not support magnetic declination. All “course over ground” data are geodetic WGS84 directions.
Mode Indicator
D
A: Autonomous GNSS fix
N: No position fix
D: Differential GNSS fix
E: Estimated/Dead reckoning fix
F: RTK float
R: RTK fixed
checksum
*57
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
16
End of sentence
3.7 GxVTG - Course over Ground and Ground Speed
Example
$GPVTG,189.32,T,,M,15.869,N,29.405,K,D*30 Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPVTG
VTG protocol header
Course over ground
189.32
degrees
Receiver’s direction of travel
Moving clockwise starting at due north (geodetic WGS84 directions)
Reference
T
True
Course over ground
degrees
Receiver’s direction of travel
Reference
M
Magnetic
Speed over ground
15.869
knots
Measured horizontal speed
Unit
N
Knots
Speed over ground
29.405
km/hr
Measured horizontal speed
Unit
K
km/hr
Mode Indicator
D
A: Autonomous GNSS fix
N: No position fix
D: Differential GNSS fix
E: Estimated/Dead reckoning fix
F: RTK float
R: RTK fixed
checksum
*30
End of sentence
3.8 GxGNS – GNSS Fix Data
Example
$GNGNS,020316.00,2446.44461,N,12100.45153,E,AAAN,24,0.61,54.5,16.3,,*53 Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GNGNS
GNS protocol header
Time
020316.00
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Latitude
2446.44661
ddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
North/South
N
N: North Latitude, S: South Latitude
Longitude
12100.45153
dddmm.mmmmm
dd: degree, mm.mmmmm: minute
East/West
E
E: East Longitude, W: West Longitude
Position Mode
AAAN
A: Autonomous GNSS fix
N: No position fix
D: Differential GNSS fix
E: Estimated/Dead reckoning fix
F: RTK float
R: RTK fixed
First character for GPS, second one
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
17
for GLONASS, Third one for Galileo, Fourth one for BeiDou
Satellites Used
24
Number of satellites used in positioning calculation (0 to 99)
HDOP
0.61
Horizontal Dilution of Precision
Altitude
54.5
meters
Altitude above mean sea level
Separation
16.3
meters
Geoid separation: difference between ellipsoid and mean sea level
Differential Age
-
Age of differential corrections (null when DGPS is not used)
Differential Station
-
ID of station providing differential corrections (null when DGPS is not used)
Checksum
*53
Checksum
End of sentence
3.9 GxGRS – GNSS Range Residuals
This messages relates to associated GGA and GSA messages. If less than 12 SVs are available, the remaining fields are output empty. If more than 12 SVs are used, only the resid-uals of the first 12 SVs are output, in order to remain consistent with the NMEA standard. In a multi-GNSS system this message will be output multiple times, once for each GNSS.
Example
$GNGRS,055709.00,1,5.9,7.6,8.5,2.8,
$GNGRS,055709.00,1,5.9,7.6,8.5,2.8,--4.2,10.8,4.2,10.8,--46.9,17.5,4.3,5.4,46.9,17.5,4.3,5.4,--19.9,*5719.9,*57
$GNGRS,0$GNGRS,055709.00,1,55709.00,1,--43.1,43.1,--70.9,70.9,--44.8,44.8,--1.4,1.4,--38.4,,,,,,,*5738.4,,,,,,,*57
ExplanationExplanation
Contents
Contents
Example
Example
Unit
Unit
Explanation
Explanation
Message
Message IDID
$GNG
$GNGRRSS
G
GRRSS protocol protocol headerheader
Time
Time
055709
055709.00.00
hhmmss.ss
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Mode
Mode
1
1
Computation method used:
Computation method used:
1:
1: Residuals were recomputResiduals were recomputed after the ed after the GGA position was computed (fixed)GGA position was computed (fixed)
Residual 1
5.9
meters
Range residuals for SVs used in navigation. The SV order matches the order from the GSA sentence
Residual 2
7.6
meters
Same as above
Residual 3
8.5
meters
Same as above
Residual 4
2.8
meters
Same as above
Residual 5
-4.2
meters
Same as above
Residual 6
10.8
meters
Same as above
Residual 7
-46.9
meters
Same as above
Residual 8
17.5
meters
Same as above
Residual 9
4.3
meters
Same as above
Residual 10
5.4
meters
Same as above
Residual 11
-19.9
meters
Same as above
Residual 12
-
meters
Same as above
Checksum
*57
Checksum
End of sentence
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
18
3.10 GxGST – GNSS Pseudo Range Error Statistics
Example
$GNGST,055526.00,43274,,,,1.2,1.2,2.1*7D Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GNGST
GST protocol header
Time
055526.00
hhmmss.ss
hh: hour, mm: minute, ss: second
Range of RMS
43274
meters
RMS value of the standard deviation of the ranges
Standard Deviation of Semi-Major Axis
-
meters
Standard deviation of semi-major axis (only supported in ADR 4.10 and later)
Standard Deviation of Semi-Minor Axis
-
meters
Standard deviation of semi-minor axis (only supported in ADR 4.10 and later)
Orientation
-
degrees
Orientation of semi-major axis (only
supported in ADR 4.10 and later)
Standard deviation of latitude error
1.2
meters
Standard deviation of latitude error
Standard deviation of longitude error
1.2
meters
Standard deviation of longitude error
Standard deviation of altitude error
2.1
meters
Standard deviation of altitude error
Checksum
*7D
Checksum
End of sentence
3.11 GxTXT – Text Transmission
Example
$GPTXT,01,01,02,u-blox ag - www.u-blox.com*50 Explanation
Contents
Example
Unit
Explanation
Message ID
$GPTXT
TXT protocol header
Number of messages
01
Total number of messages in this transmission, 01..99
Message number
01
Message number in this transmission, range 01..xx
Message type
02
Text identifier, u-blox GPS receivers specify the type of the message with this number.
00: Error
01: Warning
02: Notice
07: User
Text
u-blox ag -
Any ASCII text
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
19
www.u-blox.com
Checksum
*50
Checksum
End of sentence
3.12 GNSS Switching Commands
Switches between different GNSS systems could be done by u
Switches between different GNSS systems could be done by u--blox binary commands blox binary commands described below. described below.
Switch to GPS only
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 00 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 00 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FC 11
Switch to GPS+QZSS
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 00 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 01 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FD 1D
Switch to GPS+QZSS+SBAS
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 01 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 01 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FE 39
Switch to GPS+QZSS+GLONASS (Default)
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 00 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 01 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 01 00 01 01 FE 21
Switch to GLONASS+GPS+QZSS+SBAS
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 01 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 01 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 01 00 01 01 FF 3D
Switch to Beidou
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 00 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 00 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 00 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FC 01
Switch to GPS+Beidou
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 00 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 00 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FD 25
Switch to GPS+Beidou+QZSS+SBAS
B5 62 06 3E 2C 00 00 00 20 05 00 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 01 01 03 00 01 00 01 01 03 08 10 00 01 00 01 01 05 00 03 00 01 00 01 01 06 08 0E 00 00 00 01 01 FF 4D
Responses
ACK (Success): B5 62 05 01 02 00 06 3E 4C 75
NAK (Failure): B5 62 05 00 02 00 06 3E 4B 70
NaviSys Technology - Your Location Partner Data Sheet - GR-8017
20
Please note that
HHexadecimal values under exadecimal values under each commandeach command are binary data.are binary data.
E.g. B5 is one byte. It should NOT be sent as two characters.E.g. B5 is one byte. It should NOT be sent as two characters.
Each command is followed by either an ACK or a NAK response.Each command is followed by either an ACK or a NAK response.
ACK response: the command has been successfully exeACK response: the command has been successfully executedcuted
NAK response: the command is not valid and is not acceptedNAK response: the command is not valid and is not accepted
It takes some time (from a few to tens of seconds) before switches to alternating satellite system taking effect.
Typically, the longer it runs, the longer it takes to switch.
Save Configuration
The configuration will disappear if it was not saved and power is OFF. This command will save the configuration to BBR (battery backed RAM) so that the settings will be kept as the backup power is supplied.
B5 62 06 09 0D 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF 00 00 00
B5 62 06 09 0D 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 1D00 00 00 03 1D ABAB
UDRの初期化とキャリブレーション
GR 8017のデッドレコニングのメリットを享受するためには、UDRの初期化とキャリブレーションが必要です。 このプロセスが完了したかどうかは、u blox u center tool で UBX ESFSTATUS メッセージを確認することで、処理が完了したかどうかを知ることができます。 また、GR 8017 は固定された位置に設置する必要があります。位置が変更された場合には再校正が必要となります。 GR-8017 にコールドスタートコマンドが送られた場合や、過酷な条件でキャリブレーションが失われた場合 自動的に新しいキャリブレーションプロセスが開始されます。 初期化フェーズの期間は、GNSS信号の品質とダイナミクスに大きく依存します。 そのため車を広い駐車場などの上空が開けた平坦な場所に移動します。 初期化の手順は GR 8017のLEDが点滅して位置が確定します。 良好なGNSS受信状態での初期化およびキャリブレーションドライブは はエンジンをかけたまま数分間(例えば2分間)停車します。 次に 通常の左折・右折を3回以上行います。 そして速度が30km/h以上ので走行します。 上記の順序は変更可能ですが、校正にはすべてが必要です。 初期化が完了すると、UBX ESF STATUSメッセージのfusionModeフィールドは、次のようになります。 ESF STATUS messageが1:FUSIONに切り替わり、GNSS/Dead reckoningを組み合わせた固定値(フュージョン・ソリューション)が出力され ナビゲーション・フィルターに使用されているセンサーのキャリブレーションが開始される。 キャリブレーションは、バックグラウンドで実行される連続的なプロセスで、ナビゲーション・ソリューションの品質を向上させます。 なお、使用されているいくつかのセンサーのキャリブレーション・ステータス(UBX ESF STATUSメッセージのcalibStatus)は、使用されているセンサーによっては)は、受信機が厳しい条件で操作されると、1:CALIBRATINGに戻ってしまうことがあります。 このような場合、再校正のために最適な条件が再び観測されるまで、フュージョン・ナビゲーション計算値の不確かさが増します。 このような場合には、センサーを再校正するための最適な条件が再び観測されるまで、自立航法ソリューションの不確実性が増加します。
D-GPSデータを使用すると、近くの基準受信機またはネットワークからのリアルタイム・データを使用して、GPSの位置精度を向上させることができます。NEO-M8U受信機は、推測航法を無効にした場合にのみD-GPSをサポートします(メッセージUBX-CFG-NAVX5を使用)。D-GPSは、RTCM 10402.3の "Recommended Standard for Differential gnss "に従って、有効なデータを受信したときに起動します。RTCMは、SBASや推測航法と併用することはできず、NEO-M8UのGPS信号にのみ適用されます。RTCMの実装では、以下のRTCM 2.3メッセージをサポートしています。 Message Type: 1:Differential GPS Corrections 2:Delta Differential GPS Corrections 3:GPS Reference Station Parameters 9:GPS Partial Correction Set NEO-M8Uは、GNSSとIMUの測定値を組み合わせ、最大2Hzのレートで位置ソリューションを計算します。これらのソリューションは、標準的なNMEA、UBX-NAV-PVTおよび関連メッセージで報告されます。新しいHigh Navigation Rate出力メッセージ(UBX-HNR-PVT)は、これらの結果をIMUのみのデータで拡張し、最大30Hzのレートで正確かつ低レイテンシーの位置ソリューションを提供します。 推測航法では、モジュールに電源を投入すると同時に(つまり、GNSS固定が確立される前に)、以下の条件をすべて満たしていればナビゲーションを開始することができます。 - モジュールに電源が供給されていない状態で車両が移動していないこと - 車両が最後に使用されたときに、少なくともデッドレコニング固定が可能であった。 - 車両が最後に使用されたときからモジュールにバックアップ電源が供給されている。 センサデータは,UBX-ESF-MEAS と UBX-ESF-RAW(ハイレート)のメッセージから取得できます。各メッセージには、測定時刻が含まれています。
詳細はドキュメントUBX-13003221 (関連UBX-15028330)(NEO-M8U_DataSheet__UBX-15015679_.pdf)などをご参照下さい。