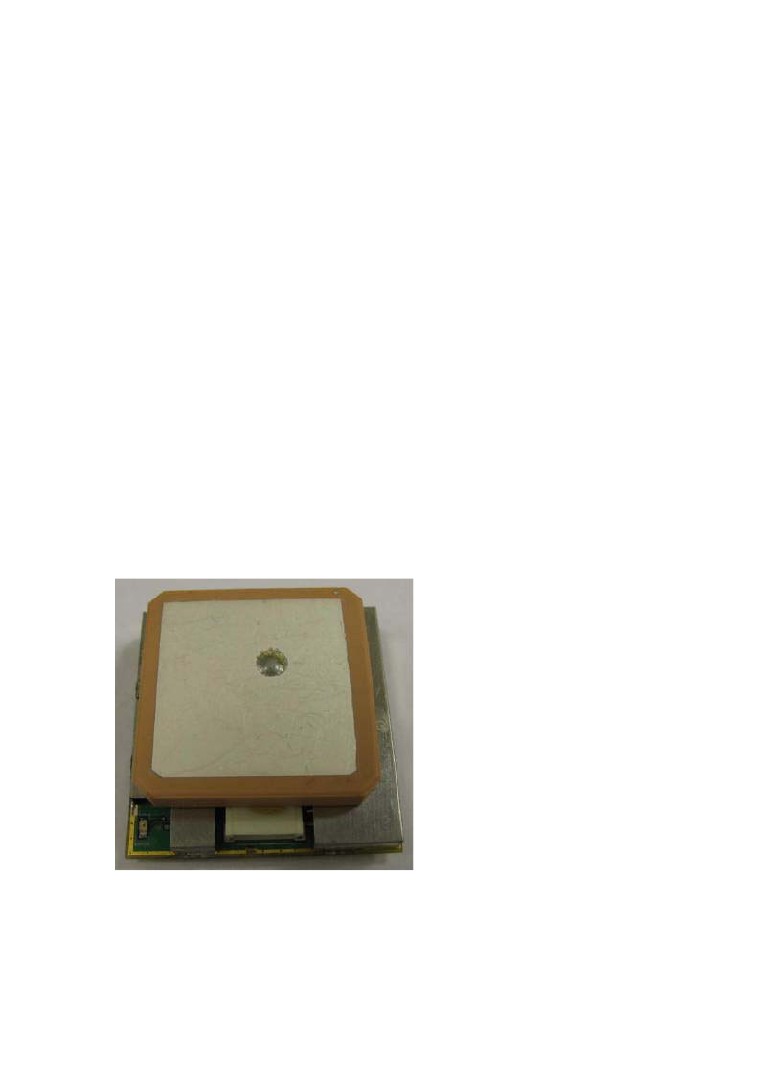
Features:
SiRF starⅢ high performance GPS Chip Set
Very high sensitivity (Tracking Sensitivity: -159 dBm)
Extremely fast TTFF (Time To First Fix) at low signal level
Support NMEA 0183 data protocol
Built-in SuperCap to reserve system data for rapid satellite acquisition
Built-in patch antenna
LED indicator for GPS fix or not fix
LED OFF:
Receiver switch off
LED ON:
No fixed, Signal searching
LED Flashing:
Position Fixed
Specification:
General
Chipset
SiRF StarⅢ
Frequency
L1, 1575.42 MHz
C/A code
1.023 MHz chip rate
Channels
20 channel all-in-view tracking
Sensitivity
-159 dBm
Accuracy
Position
10 meters, 2D RMS
5 meters, 2D RMS, WAAS enabled
Velocity
0.1 m/s
Time
1us synchronized to GPS time
Datum
Default
WGS-84
Acquisition Time
Reacquisition
0.1 sec., average
Hot start
1 sec., average
Warm start
38 sec., average
Cold start
42 sec., average
Dynamic Conditions
Altitude
18,000 meters (60,000 feet) max
Velocity
515 meters /second (1000 knots) max
Acceleration
Less than 4g
Jerk
20m/sec **3
Power
Main power input
4.5V ~ 6.5V DC input
Power consumption
44mA
Protocol
Electrical level
TTL level, Output voltage level: 0V ~ 2.85V
RS-232 level
Baud rate
4,800 bps
Output message
NMEA 0183 GGA, GSA, GSV, RMC, VTG, GLL
Physical Characteristics
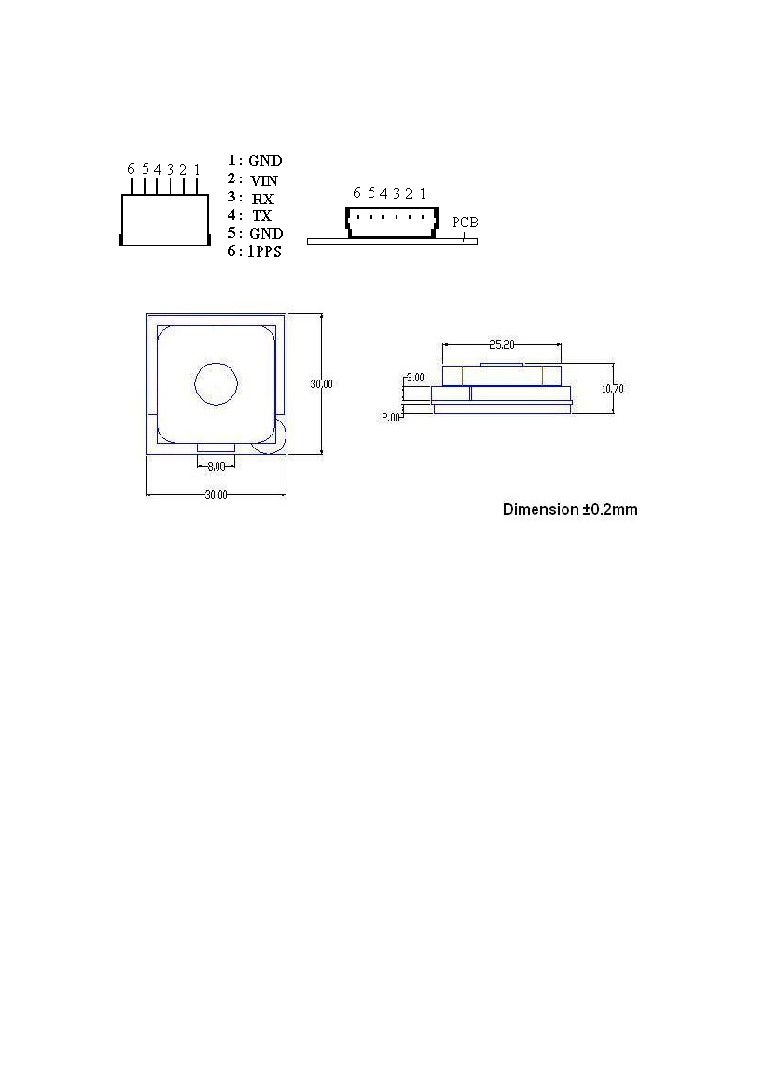
Dimension
30mm*30mm*10.5mm ±0.2mm
Operating temperature
-40℃ to +85℃
Pin Assignment
Pin description
* VIN (DC power input):
This is the main DC supply for a 4.5V ~6.5 DC input power.
* TX:
This is the main transmits channel for outputting navigation and measurement
data to user’ s navigation software or user written software.
* RX:
This is the main receive channel for receiving software commands to the engine
board from SiRFdemo software or from user written software.
* GND:
GND provides the ground for the engine board. Connect all grounds.
* 1PPS
This pin provides one pulse-per-second output from the engine board that is
synchronized to GPS time.
SOFTWARE COMMAND
NMEA Output Command
GGA-Global Positioning System Fixed Data
Table B-2 contains the values for the following example:
$GPGGA,161229.487,3723.2475,N,12158.3416,W,1,07,1.0,9.0,M,,,,0000*18
Table B-2 GGA Data Format
Name
Example
Units
Description
Message ID
$GPGGA
GGA protocol header
UTC Time
161229.487
hhmmss.sss
Latitude
3723.2475
ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator
N
N=north or S=south
Longitude
12158.3416
dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator
W
E=east or W=west
Position Fix Indicator
1
See Table B-3
Satellites Used
07
Range 0 to 12
HDOP
1.0
Horizontal Dilution of Precision
MSL Altitude1
9.0
meters
Units
M
meters
Geoid Separation1
meters
Units
M
meters
Age of Diff. Corr.
second
Null fields when DGPS is not used
Diff. Ref. Station ID
0000
Checksum
*18
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
SiRF Technology Inc. does not support geoid corrections. Values are WGS84 ellipsoid heights.
Table B-3 Position Fix Indicator
Value
Description
0
Fix not available or invalid
1
GPS SPS Mode, fix valid
2
Differential GPS, SPS Mode , fix valid
3
GPS PPS Mode, fix valid
GLL-Geographic Position-Latitude/Longitude
Table B-4 contains the values for the following example:
$GPGLL,3723.2475,N,12158.3416,W,161229.487,A*2C
Table B-4 GLL Data Format
Name
Example
Units
Description
Message ID
$GPGLL
GLL protocol header
Latitude
3723.2475
ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator
n
N=north or S=south
Longitude
12158.3416
dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator
W
E=east or W=west
UTC Position
161229.487
hhmmss.sss
Status
A
A=data valid or V=data not valid
Checksum
*2C
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
GSA-GNSS DOP and Active Satellites
Table B-5 contains the values for the following example:
$GPGSA,A,3,07,02,26,27,09,04,15,,,,,,1.8,1.0,1.5*33
Table B-5 GSA Data Format
Name
Example
Units
Description
Message ID
$GPGSA
GSA protocol header
Mode1
A
See Table B-6
Mode2
3
See Table B-7
Satellite Used1
07
Sv on Channel 1
Satellite Used1
02
Sv on Channel 2
…
Satellite Used1
Sv on Channel 12
PDOP
1.8
Position dilution of Precision
HDOP
1.0
Horizontal dilution of Precision
VDOP
1.5
Vertical dilution of Precision
Checksum
*33
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
1.
Satellite used in solution.
Table B-6 Mode1
Value
Description
M
Manual-forced to operate in 2D or 3D mode
A
2Dautomatic-allowed to automatically switch 2D/3D
Table B-7 Mode 2
Value
Description
1
Fix Not Available
2
2D
3
3D
GSV-GNSS Satellites in View
Table B-8 contains the values for the following example:
$GPGSV,2,1,07,07,79,048,42,02,51,062,43,26,36,256,42,27,27,138,42*71
$GPGSV,2,2,07,09,23,313,42,04,19,159,41,15,12,041,42*41
Table B-8 GSV Data Format
Name
Example
Description
Message ID
$GPGSV
GSV protocol header
Number of Messages1
2
Range 1 to 3
Message Number1
1
Range 1 to 3
Satellites in View
07
Satellite ID
07
Channel 1(Range 1 to 32)
Elevation
79
degrees
Channel 1(Maximum90)
Azimuth
048
degrees
Channel 1(True, Range 0 to 359)
SNR(C/No)
42
dBHz
Range 0 to 99,null when not tracking
…….
…….
Satellite ID
27
Channel 4 (Range 1 to 32)
Elevation
27
Degrees
Channel 4(Maximum90)
Azimuth
138
Degrees
Channel 4(True, Range 0 to 359)
SNR(C/No)
42
dBHz
Range 0 to 99,null when not tracking
Checksum
*71
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
Depending on the number of satellites tracked multiple messages of GSV data may be required.
RMC-Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data
Table B-10 contains the values for the following example:
$GPRMC,161229.487,A,3723.2475,N,12158.3416,W,0.13,309.62,120598,,*10
Table B-10 RMC Data Format
Name
Example
Units
Description
Message ID
$GPRMC
RMC protocol header
UTC Time
161229.487
hhmmss.sss
Status
A
A=data valid or V=data not valid
Latitude
3723.2475
ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator
N
N=north or S=south
Longitude
12158.3416
dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator
W
E=east or W=west
Speed Over Ground
0.13
knots
Course Over Ground
309.62
degrees
True
Date
120598
ddmmyy
Magnetic Variation2
degrees
E=east or W=west
Checksum
*10
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
SiRF Technology Inc. does not support magnetic declination. All “course over ground” data are
geodetic WGS48 directions.
VTG-Course Over Ground and Ground Speed
$GPVTG,309.62,T,,M,0.13,N,0.2,K*6E
Name
Example
Units
Description
Message ID
$GPVTG
VTG protocol header
Course
309.62
degrees
Measured heading
Reference
T
True
Course
degrees
Measured heading
Reference
M
Magnetic
Speed
0.13
knots
Measured horizontal speed
Units
N
Knots
Speed
0.2
Km/hr
Measured horizontal speed
Units
K
Kilometers per hour
Checksum
*6E
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
NMEA Input Command
A). Set Serial Port
ID:100
Set PORTA parameters and protocol
This command message is used to set the protocol(SiRF Binary, NMEA, or
USER1) and/or the communication parameters(baud, data bits, stop bits, parity).
Generally,this command would be used to switch the module back to SiRF Binary
protocol mode where a more extensive command message set is available. For
example,to change navigation parameters. When a valid message is received,the
parameters will be stored in battery backed SRAM and then the receiver will restart
using the saved parameters.
Format:
$PSRF100,<protocol>,<baud>,<DataBits>,<StopBits>,<Parity>*CKSUM
<CR><LF>
<protocol>
0=SiRF Binary, 1=NMEA, 4=USER1
<baud>
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
<DataBits>
8,7. Note that SiRF protocol is only valid f8
Data bits
<StopBits>
0,1
<Parity>
0=None, 1=Odd, 2=Even
Example 1: Switch to SiRF Binary protocol at 9600,8,N,1
$PSRF100,0,9600,8,1,0*0C<CR><LF>
Example 2: Switch to User1 protocol at 38400,8,N,1
$PSRF100,4,38400,8,1,0*38<CR><LF>
**Checksum Field: The absolute value calculated by exclusive-OR the
8 data bits of each character in the Sentence,between, but
excluding
“$” and
“*”. The hexadecimal value of the most
significant and least significant 4 bits of the result are convertted
to two ASCII characters (0-9,A-F) for transmission. The most
significant character is transmitted first.
**<CR><LF>
: Hex 0D 0A
B). Navigation lnitialization ID
101 Parameters required for
start
This command is used to initialize the module for a warm start, by providing current
position (in X, Y, Z coordinates),clock offset, and time. This enables the receiver
to search for the correct satellite signals at the correct signal parameters. Correct
initialization parameters will enable the receiver to acquire signals more quickly, and
thus, produce a faster navigational solution.
When a valid Navigation Initialization command is received, the receiver will restart
using the input parameters as a basis for satellite selection and acquisition.
Format
$PSRF101,<X>,<Y>,<Z>,<ClkOffset>,<TimeOfWeek>,<WeekNo>,<chnlCount>,<R
esetCfg>
*CKSUM<CR><LF>
<X>
X coordinate position
INT32
<Y>
Y coordinate position
INT32
<Z>
Z coordinate position
INT32
<ClkOffset>
Clock offset of the receiver in Hz, Use 0 for
last saved value if available. If this is
unavailable, a default value of 75000 for
GSP1, 95000 for GSP 1/LX will be used.
INT32
<TimeOf Week>
GPS Time Of Week
UINT32
<WeekNo>
GPS Week Number
UINT16
( Week No and Time Of Week calculation
from UTC time)
<chnlCount>
Number of channels to use.1-12. If your
CPU throughput is not high enough, you
could decrease needed throughput by
reducing the number of active channels
UBYTE
<ResetCfg>
bit mask
0×01=Data Valid warm/hotstarts=1
0×02=clear ephemeris warm start=1
0×04=clear memory. Cold start=1
UBYTE
Example: Start using known position and time.
$PSRF101,-2686700,-4304200,3851624,96000,497260,921,12,3*7F
C). Set DGPS Port ID:102 Set PORT B parameters for DGPS input
This command is used to control Serial Port B that is an input only serial port
used to receive
RTCM differential corrections.
Differential receivers may output corrections using different
communication parameters.
The default communication parameters for PORT B are 9600
Baud, 8data bits, 0 stop bits, and no parity.
If a DGPS receiver is used which has different communication parameters, use
this command to allow the receiver to correctly decode the data. When a valid
message is received, the parameters will be stored in battery backed SRAM and
then the receiver will restart using the saved parameters.
Format:
$PSRF102,<Baud>,<DataBits>,<StopBits>,<Parity>*CKSUM<CR><LF>
<baud>
1200,2400,4800,9600,19200,38400
<DataBits>
8
<StopBits>
0,1
<Parity>
0=None,Odd=1,Even=2
Example: Set DGPS Port to be 9600,8,N,1
$PSRF102,9600,8,1.0*12
D). Query/Rate Control ID:103 Query standard NMEA message and/or set
output rate
This command is used to control the output of standard NMEA message GGA,
GLL, GSA, GSV
RMC, VTG. Using this command message, standard NMEA message may be
polled once, or setup for periodic output. Checksums may also be enabled
or disabled depending on the needs of the receiving program. NMEA
message settings are saved in battery backed memory for each entry when the
message is accepted.
Format:
$PSRF103,<msg>,<mode>,<rate>,<cksumEnable>*CKSUM<CR><LF>
<msg>
0=GGA,1=GLL,2=GSA,3=GSV,4=RMC,5=VTG
<mode>
0=SetRate,1=Query
<rate>
Output every <rate>seconds, off=0,max=255
<cksumEnable>
0=disable Checksum,1=Enable checksum
for specified message
Example 1: Query the GGA message with checksum enabled
$PSRF103,00,01,00,01*25
Example 2: Enable VTG message for a 1Hz constant output with checksum
enabled
$PSRF103,05,00,01,01*20
Example 3: Disable VTG message
$PSRF103,05,00,00,01*21
E). LLA Navigation lnitialization ID:104 Parameters required to start
using Lat/Lon/Alt
This command is used to initialize the module for a warm start, by providing
current position (in Latitude, Longitude, Altitude coordinates), clock offset, and
time. This enables the receiver to search for the correct satellite signals at
the correct signal parameters. Correct initialization parameters will enable
the receiver to acquire signals more quickly, and thus, will produce a faster
navigational soution.
When a valid LLANavigationInitialization command is received,the receiver will
restart using the input parameters as a basis for satellite selection and acquisition.
Format:
$PSRF104,<Lat>,<Lon>,<Alt>,<ClkOffset>,<TimeOfWeek>,<WeekNo>,
<ChannelCount>, <ResetCfg>*CKSUM<CR><LF>
<Lat>
Latitude position, assumed positive north of equator and
negative south of equator float, possibly signed
<Lon>
Longitude position, it is assumed positive east of Greenwich
and negative west of Greenwich
Float, possibly signed
<Alt>
Altitude position
float, possibly signed
<ClkOffset>
Clock Offset of the receiver in Hz, use 0 for last saved value if
available. If this is unavailable, a default value of 75000 for
GSP1, 95000 for GSP1/LX will be used.
INT32
<TimeOfWeek> GPS Time Of Week
UINT32
<WeekNo>
GPS Week Number
UINT16
<ChannelCount> Number of channels to use. 1-12
UBYTE
<ResetCfg>
bit mask
0×01=Data Valid warm/hot starts=1
0×02=clear ephemeris warm start=1
0×04=clear memory. Cold start=1
UBYTE
Example: Start using known position and time.
$PSRF104,37.3875111,-121.97232,0,96000,237759,922,12,3*37
F). Development Data On/Off
ID:105
Switch Development Data
Messages On/Off
Use this command to enable development debug information if you are having
trouble getting commands accepted. Invalid commands will generate debug
information that should enable the user to determine the source of the
command rejection. Common reasons for input command rejection are invalid
checksum or parameter out of specified range. This setting is not preserved
across a module reset.
Format:
$PSRF105,<debug>*CKSUM<CR><LF>
<debug>
0=Off,1=On
Example: Debug On
$PSRF105,1*3E
Example: Debug Off
$PSRF105,0*3F
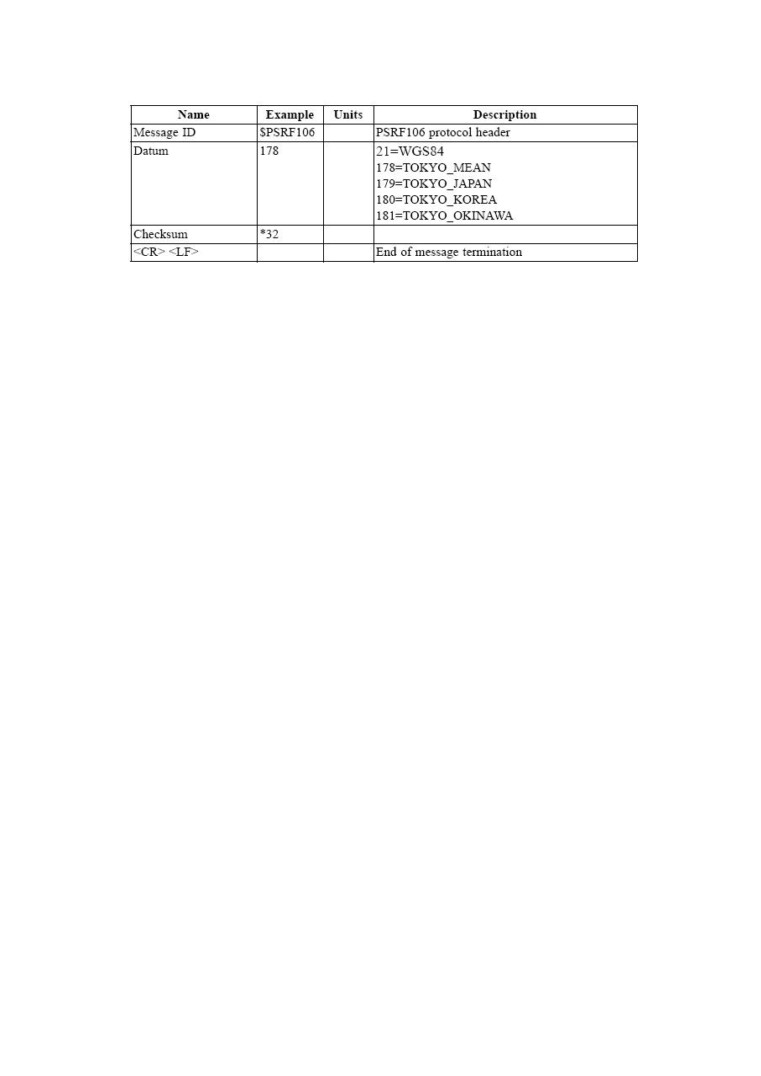
G). Select Datum
ID:106
Selection of datum to be used for coordinate
Transformations
GPS receivers perform initial position and velocity calculations using an earth-centered
earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinate system. Results may be converted to an earth model (geoid)
defined by the selected datum. The default datum is WGS 84 (World Geodetic System 1984)
which provides a worldwide common grid system that may be translated into local coordinate
systems or map datums. (Local map datums are a best fit to the local shape of the earth and not
valid worldwide.)
Examples:
Datum select TOKYO_MEAN
$PSRF106,178*32